In the aftermath of the Second World War, the European Economic Community was formed, a precursor of the European Union. Initially, the EEC was designed to boost economic cooperation among six countries. It has now grown to include 22 nations, creating a giant single market, or internal market. But what was its purpose? What are its five main aims? And how does it function? To answer this question, we’ve created a short summary of the EEC.
How many nations originally joined the EU in 1993?
Originally, 12 countries joined the EU. Great Britain, France, Germany, Spain, Portugal, Italy, Greece, Denmark, Luxembourg, and Belgium were the first ten countries to ratify the treaty. Other countries later joined, including Austria, Finland, and Sweden. The European Union’s membership has grown steadily over the years, with more than forty member states and more than a thousand nationalities.
The European Union, or EU, was formed on 1 November 1993 with the signing of the Maastricht Treaty. The Treaty’s founding principles include greater cooperation among member states and the creation of a single currency system called the euro. The Treaty was amended several times between 1993 and 2009, and there are now more than thirty member states than when it was first formed. Although this is an incomplete list, these countries make up about a quarter of the EU’s total membership.
The first round of negotiations started on 1 February 1993. The applicant countries were required to accept the acquis communautaire and the European Treaty before being granted membership. However, several countries requested derogations from these rules. These derogations made it difficult to decide on a common budget and set fishing quotas. In addition, some countries wished to join the EU quickly, such as the United Kingdom and Germany, as well as some Nordic nations. Consequently, last-minute concessions were made in the area of farm subsidies and fisheries.
What is the European Union summary?
There are a number of documents produced by the European Union. These documents include policy statements and working papers that provide information on a wide variety of topics. These documents are usually what you will come across when you do your research on a particular issue. However, you should know that they are not binding. The European Union has many other bodies and institutions that make decisions for the whole organization. Here is a brief overview of their role and responsibilities.
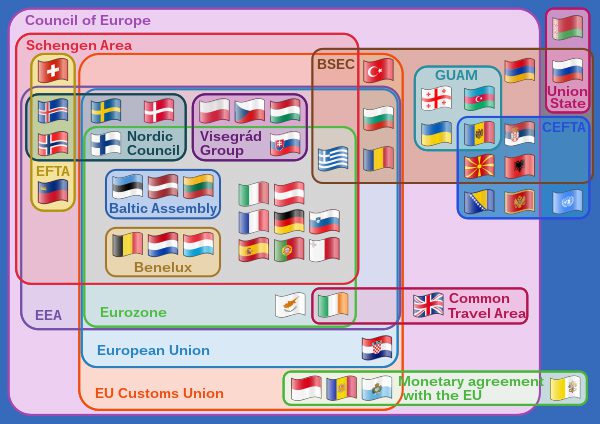
The Council of Europe is a body of 46 European nations. It was formed to protect the rule of law, promote democracy, and protect human rights in the continent. The Council of Europe is the institution that makes policy for the EU, whose member states are based in Europe. Today, the EU has 27 members, with some delegating their sovereignty to the body. No country has ever been admitted to the EU without first belonging to the Council of Europe.
What are the top five aims of the EU?
While the European Union was founded as a mercantilist organisation in the 1950s, it has developed into a more holistic entity. Today, the European Union aims to combat social exclusion, safeguard cultural diversity, promote scientific and technological progress, and support the values of inclusion, tolerance, and solidarity. In 2012, the EU received the Nobel Peace Prize, a recognition of its efforts to bring peace and prosperity to Europe.
The digital single market is a key area for EU policies, especially given the growing digitization of European economies. The EU must focus on fostering a continuous dialogue among its member states and foster a substantive public-private dialogue to safeguard its technological base. In particular, it needs to invest in developing dual-use technologies and cooperate with non-EU nations to advance its agenda. A new white paper on AI outlines some of the priorities for future efforts, including how the EU can encourage more investments in research and development in its member states.
The EU is a fusion of many past efforts to integrate Europe. Following World War II, western European nations sought closer economic and social ties with each other, while ensuring military security and achieving lasting reconciliation between Germany and France. The Treaty of Paris was signed in 1951, establishing the European Coal and Steel Community and a Commission. The EEC now has four governing institutions: the commission, the ministerial council, the assembly, and the court.
What is the function of European Union?
The EU is a political and economic organization that governs the member states. The European Commission is the executive arm of the EU. Its mandate is to promote the common interest of the Union through appropriate initiatives and the application of EU law, which is controlled by the Court of Justice of the European Union. The Commission is responsible for executing budgets and managing programmes and exercises its coordinating, executive, and management functions. It also acts as the external representative of the EU.
While the EU holds most of the authority in the single market, member states still retain more control over major policy areas such as immigration, defense, and citizenship. This multi-level approach to government reflects the advantages of scale, and differences between countries and communities nudge policymaking downward. But what is the function of the European Union?? today’s answer will be helpful for all EU citizens. In order to answer the question, let’s review the EU’s structure.
What are the 4 benefits of the EU?
The EU has many advantages, ranging from free movement to increased trade and employment opportunities. Its single market has helped a number of smaller nations develop their economies, and people can use EU qualifications in other member countries. In addition, the EU’s mutual recognition of safety standards and rules has helped reduce the cost for firms and encouraged the growth of small and medium businesses. The EU’s social charter guarantees workers’ rights, including maximum working hours, collective bargaining rights, and fair pay.
The EU has helped heal Europe’s divisions, and has become a strong economic and political force. In the past, many countries within the continent were at loggerheads with each other, but that’s no longer the case. Europe has healed from the wounds of World Wars and has a reputation for peace. The EU has also won the Nobel Peace Prize for promoting international co-operation and peace. Today, many Eastern European countries want to join the EU.
What is the European Union short summary?
The EU is a group of 27 member states. The EU is run by a governing council. Each member state appoints a representative to the European Parliament. Members of the European Parliament are responsible for passing laws and overseeing the Commission. They also negotiate the EU budget and oversee the European Commission. The European Parliament is currently led by Maltese politician Roberta Metsola. The European Council is the EU’s legislative body. It comprises government ministers from all member states. Decisions made by the council are often required to be unanimous, though they can be voted down if necessary.
The Council of the EU consists of national governments and the European Commission. The European Council meets at least twice a year and defines the EU’s long-term agenda. Every six months, a different member state holds the presidency. Before the Lisbon Treaty, the presidency was rotated. Today, the presidency is a permanent office. The head of the European Council is chosen by the members of the EU. Its functions include:
What is European Union introduction?
A quick EU introduction can help you learn about this unique political organization. The EU is a group of 27 nations, all of which have agreed to share certain economic and social policies. In the early 21st century, this group expanded to include countries in central and eastern Europe, including Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Portugal, Slovakia, Slovenia, and Sweden. The EU operates through a system of intergovernmentally negotiated decisions between the member states. The European Parliament is elected every five years by the citizens of these states.
The European Union is structured like a federation, but lacks the power of coercion. Instead, it relies on its member states to enforce its policies. This structure is also more decentralized than a typical state, since powers are distributed among the nation states. As such, the European Union is more like a federation, which means that it has a more democratic and decentralized structure than the typical state.
Who joined EU first?
Who joined the European Union first? The EU is a political and economic union. In the aftermath of World War II, the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) was created. This community was then expanded to include ten other member states in 1957. In 1972, Ireland, the United Kingdom, and Denmark joined, and seven years later, the European Parliament was established. The European Union has expanded its powers with the Treaty of Lisbon, which increased judicial cooperation and border control. The ECSC was later renamed the European Economic Community, and the member states have been grouped by the three pillars.
The Copenhagen criteria is the basis for membership in the EU. The criteria, which were developed at a 1993 European Council meeting in Copenhagen, include a stable democracy, respect for human rights, and acceptance of EU law. Each new member state must meet the Copenhagen criteria in order to become an EU member, and they must also agree to abide by the EU’s rules. In addition to the Copenhagen criteria, the EU has the right to decide whether a country is eligible to become a member of the EU.
About The Author

Tess Mack is a social media expert who has fallen down more times than she can count. But that hasn't stopped her from becoming one of the most well-known Twitter advocates in the world. She's also a web nerd and proud travel maven, and is considered to be one of the foremost experts on hipster-friendly social media. Tess loves sharing interesting facts with her followers, and believes that laughter is the best way to connect with people.