Last Updated on July 23, 2023
Short Answer
The hormone that has intracellular receptor sites is cortisol. These receptor sites are located inside the cell, specifically in the cytoplasm or nucleus. When cortisol binds to its intracellular receptor, it forms a hormone-receptor complex that can directly affect gene expression and regulate various cellular processes. This mechanism allows cortisol to have a direct and profound impact on the body’s stress response, metabolism, immune function, and other physiological functions.Understanding the Role of Hormones with Intracellular Receptor Sites
Hormones play a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes in the body. One important aspect of hormone function is their interaction with intracellular receptor sites. These receptor sites, located inside the cell, allow hormones to bind and initiate specific cellular responses. In this article, we will delve into the significance of intracellular receptor sites in hormone function, exploring the mechanism of action for hormones that utilize these sites. We will also discuss common hormones that rely on intracellular receptor sites and their impact on cellular processes. Furthermore, we will uncover the connection between hormones with intracellular receptor sites and gene expression, as well as their role in development, growth, metabolism, and energy balance. Finally, we will explore the implications of hormones with intracellular receptor sites in disease and treatment. Join us as we unravel the intricate interplay between hormones and intracellular receptor sites.
Understanding the Role of Hormones with Intracellular Receptor Sites
Hormones play a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes in the body. One important aspect of hormone function is their interaction with intracellular receptor sites. These receptor sites are located inside the cell, allowing hormones to directly affect cellular processes. Understanding the significance of intracellular receptor sites in hormone function is essential in comprehending the overall impact of hormones on the body.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Intracellular receptor sites allow hormones to bind and activate specific cellular responses.
- Hormones with intracellular receptor sites can directly affect gene expression and protein synthesis.
- Common hormones that utilize intracellular receptor sites include steroid hormones, thyroid hormones, and vitamin D.
- Hormones with intracellular receptor sites play a crucial role in cellular processes such as growth, development, metabolism, and energy balance.
- Understanding the interplay between hormones and intracellular receptor sites is important in the context of disease and treatment.
Overall, hormones with intracellular receptor sites have a profound impact on cellular processes and play a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis in the body.
The Significance of Intracellular Receptor Sites in Hormone Function
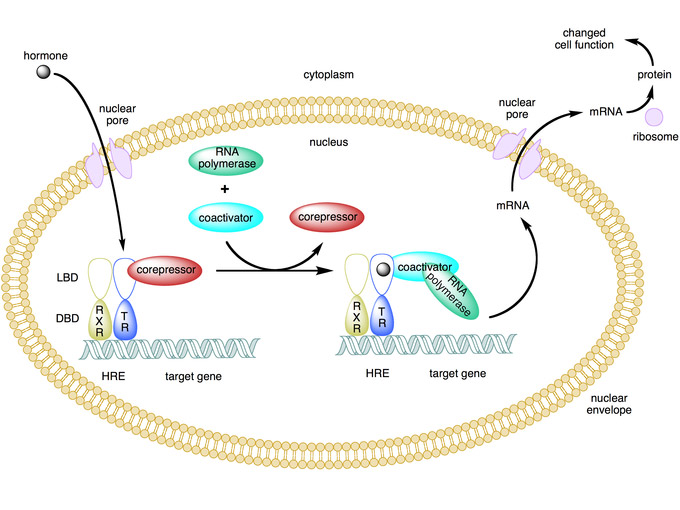
Intracellular receptor sites play a crucial role in the functioning of hormones within the body. These receptor sites are located inside the cell, allowing hormones to directly interact with the cell’s DNA and initiate various cellular processes. This mechanism of action is in contrast to hormones that utilize membrane-bound receptors, which rely on secondary messengers to transmit signals.
Understanding the significance of intracellular receptor sites is essential in comprehending the intricate interplay between hormones and cellular processes. By binding to these receptor sites, hormones can regulate gene expression, leading to the production of specific proteins that are vital for various physiological functions.
Furthermore, hormones with intracellular receptor sites have a direct impact on cellular processes such as metabolism, growth, and development. Through their interaction with DNA, these hormones can modulate the expression of genes involved in these processes, ultimately influencing an individual’s overall health and well-being.
Common Hormones That Utilize Intracellular Receptor Sites
Hormones play a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes in the body. Some hormones utilize intracellular receptor sites to exert their effects. Here are some common hormones that utilize intracellular receptor sites:
- Estrogen: Estrogen is a hormone that is primarily responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system. It binds to intracellular receptors in target cells to regulate gene expression and promote the growth and development of female secondary sexual characteristics.
- Testosterone: Testosterone is a hormone that is primarily responsible for the development and regulation of the male reproductive system. It binds to intracellular receptors in target cells to regulate gene expression and promote the growth and development of male secondary sexual characteristics.
- Cortisol: Cortisol is a hormone that is involved in the body’s response to stress. It binds to intracellular receptors in target cells to regulate gene expression and modulate the immune response and metabolism.
- Thyroid hormones: Thyroid hormones, such as thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), are involved in regulating metabolism and energy balance. They bind to intracellular receptors in target cells to regulate gene expression and control metabolic rate.
- Vitamin D: Vitamin D is a hormone that is involved in calcium and phosphate metabolism. It binds to intracellular receptors in target cells to regulate gene expression and promote the absorption of calcium and phosphate from the intestines.
These are just a few examples of hormones that utilize intracellular receptor sites. Understanding the role of these hormones and their mechanisms of action is essential for understanding the complex interplay between hormones and cellular processes.
Unveiling the Connection Between Hormones with Intracellular Receptor Sites and Gene Expression
Hormones with intracellular receptor sites play a crucial role in regulating gene expression, which is the process by which information from a gene is used to create a functional product, such as a protein. The connection between hormones and gene expression is complex and involves several steps:
- Hormone binding: When a hormone with an intracellular receptor site enters a cell, it binds to its specific receptor located inside the cell.
- Receptor activation: The binding of the hormone to its receptor triggers a series of events that lead to the activation of the receptor.
- Transcription: Once activated, the receptor moves into the nucleus of the cell and binds to specific regions of DNA called hormone response elements (HREs).
- Gene expression: The binding of the receptor to HREs initiates the transcription of specific genes, resulting in the production of messenger RNA (mRNA).
- Translation: The mRNA is then translated into proteins, which carry out various cellular functions.
This connection between hormones and gene expression allows hormones to regulate the production of specific proteins in response to various physiological and environmental cues. By controlling gene expression, hormones with intracellular receptor sites can influence a wide range of cellular processes, including growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
The Role of Hormones with Intracellular Receptor Sites in Development and Growth
Hormones with intracellular receptor sites play a crucial role in the development and growth of organisms. These hormones, such as growth hormone and thyroid hormone, bind to receptors inside the cell, triggering a cascade of events that ultimately lead to changes in gene expression and cellular processes.
During development, these hormones are responsible for regulating the growth and differentiation of cells, tissues, and organs. They control the timing and extent of growth, ensuring that organisms reach their full potential. Without these hormones, proper development and growth would be compromised.
In addition to development, hormones with intracellular receptor sites also play a role in postnatal growth. They regulate the growth of bones, muscles, and other tissues, ensuring that individuals reach their adult size and maintain proper body proportions.
Furthermore, these hormones are involved in the regulation of puberty. They stimulate the development of secondary sexual characteristics and the maturation of reproductive organs, allowing individuals to reach sexual maturity.
In summary, hormones with intracellular receptor sites are essential for the proper development and growth of organisms. They regulate various cellular processes and ensure that individuals reach their full potential in terms of size, shape, and reproductive capacity.
How Hormones with Intracellular Receptor Sites Regulate Metabolism and Energy Balance
Hormones with intracellular receptor sites play a crucial role in regulating metabolism and energy balance in the body. These hormones, such as thyroid hormones and glucocorticoids, bind to receptors inside the cell, initiating a cascade of events that ultimately affect metabolic processes.
One important way in which these hormones regulate metabolism is by influencing the rate at which cells produce and consume energy. For example, thyroid hormones increase the metabolic rate by stimulating the production of heat and energy in cells. This leads to an increase in overall energy expenditure.
In addition to regulating energy production, hormones with intracellular receptor sites also play a role in energy storage and utilization. For instance, insulin, a hormone that binds to intracellular receptors, promotes the uptake and storage of glucose in cells, thereby regulating blood sugar levels and ensuring a steady supply of energy.
Furthermore, hormones with intracellular receptor sites can also affect appetite and food intake. Leptin, a hormone produced by fat cells, acts on intracellular receptors in the hypothalamus to regulate hunger and satiety signals. This helps to maintain a balance between energy intake and expenditure.
In summary, hormones with intracellular receptor sites are essential for regulating metabolism and energy balance in the body. By influencing energy production, storage, and utilization, these hormones ensure that the body maintains a steady supply of energy for its various functions.
The Implications of Hormones with Intracellular Receptor Sites in Disease and Treatment
Hormones with intracellular receptor sites play a crucial role in various diseases and their treatment. Understanding the implications of these hormones is essential for developing effective therapeutic strategies.
One important implication is the role of these hormones in cancer. Certain hormones, such as estrogen and testosterone, can bind to intracellular receptors in cancer cells, promoting their growth and proliferation. This knowledge has led to the development of hormone therapy, which aims to block the action of these hormones and inhibit cancer progression.
Another implication is the impact of these hormones on metabolic disorders. Hormones like insulin and glucagon, which utilize intracellular receptor sites, are involved in regulating blood sugar levels. Dysfunction in these hormones can lead to conditions such as diabetes. Understanding the mechanisms of action of these hormones can help in developing targeted therapies for managing metabolic disorders.
Furthermore, hormones with intracellular receptor sites have implications in mental health disorders. Hormones like serotonin and dopamine, which act on intracellular receptors in the brain, play a crucial role in mood regulation. Imbalances in these hormones have been linked to conditions such as depression and anxiety. Targeting these intracellular receptors can be a potential approach for developing novel treatments for mental health disorders.
In conclusion, hormones with intracellular receptor sites have significant implications in disease development and treatment. Understanding the mechanisms of action of these hormones can pave the way for the development of targeted therapies for various conditions, including cancer, metabolic disorders, and mental health disorders.
The Intricate Interplay Between Hormones and Intracellular Receptor Sites
The intricate interplay between hormones and intracellular receptor sites is a fascinating area of study in the field of endocrinology. Throughout this article, we have explored the role of hormones with intracellular receptor sites and their significance in various cellular processes. These hormones, such as cortisol and estrogen, bind to receptors inside the cell, triggering a cascade of events that ultimately affect gene expression and cellular function.
Understanding the mechanism of action for hormones with intracellular receptor sites is crucial in comprehending their impact on development, growth, metabolism, and energy balance. These hormones play a vital role in regulating these processes, ensuring the proper functioning of the body.
Moreover, hormones with intracellular receptor sites have implications in disease and treatment. Dysregulation of these hormones can lead to various disorders, and targeting their receptors has become a therapeutic approach in managing certain conditions.
In conclusion, the intricate interplay between hormones and intracellular receptor sites is a complex and essential aspect of endocrinology. Further research in this field will continue to shed light on the mechanisms and implications of these hormones, ultimately leading to advancements in disease management and treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are intracellular receptor sites?
Which hormones have intracellular receptor sites?
How do hormones with intracellular receptor sites function?
What is the significance of intracellular receptor sites in hormone function?
What impact do hormones with intracellular receptor sites have on cellular processes?
How do hormones with intracellular receptor sites regulate metabolism and energy balance?
What is the connection between hormones with intracellular receptor sites and gene expression?
How do hormones with intracellular receptor sites impact development and growth?
What are the implications of hormones with intracellular receptor sites in disease and treatment?
What is the intricate interplay between hormones and intracellular receptor sites?
About The Author

Wendy Lee is a pop culture ninja who knows all the latest trends and gossip. She's also an animal lover, and will be friends with any creature that crosses her path. Wendy is an expert writer and can tackle any subject with ease. But most of all, she loves to travel - and she's not afraid to evangelize about it to anyone who'll listen! Wendy enjoys all kinds of Asian food and cultures, and she considers herself a bit of a ninja when it comes to eating spicy foods.