Last Updated on July 27, 2023
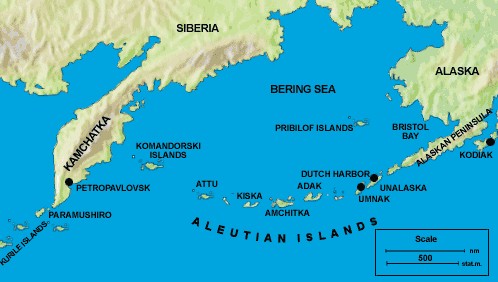
The Aleutian Islands, a chain of volcanic islands stretching across the northern Pacific Ocean, have a rich geological history that dates back millions of years. These islands, known for their stunning landscapes and unique ecosystems, were formed through a combination of tectonic activity, volcanic eruptions, and erosion processes. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating story of how the Aleutian Islands came to be, exploring the role of plate tectonics, the impact of volcanic activity, and the forces of erosion and weathering. We will also examine the biodiversity of these islands and the human presence that has shaped their history. Join us on this journey through time as we uncover the mysteries of the Aleutian Islands.
Geological history of the Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands have a fascinating geological history that spans millions of years. Here are some key points:
- The islands were formed through a process known as subduction, where one tectonic plate is forced beneath another.
- This subduction zone is part of the larger Pacific Ring of Fire, which is known for its high volcanic and seismic activity.
- The Aleutian Islands are located at the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate.
- Geologists believe that the islands began forming around 40 million years ago.
- Over time, the subduction of the Pacific Plate beneath the North American Plate has led to the formation of a chain of volcanic islands.
It is important to note that the geological processes that formed the Aleutian Islands are still ongoing today. This means that the islands are constantly changing and evolving.
Understanding the geological history of the Aleutian Islands is crucial for studying their unique ecosystems and the impact of human activities on these fragile environments.
Tectonic activity in the region
The Aleutian Islands, located in the northern Pacific Ocean, are a result of intense tectonic activity in the region. This activity is primarily driven by the collision of two major tectonic plates – the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. The Pacific Plate is subducting beneath the North American Plate, creating a subduction zone along the Aleutian Trench.
This subduction zone is characterized by intense seismic activity, with frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. The movement of the plates causes the crust to buckle and fold, leading to the formation of mountain ranges and volcanic arcs. The Aleutian Islands are part of this volcanic arc, which stretches over 1,200 miles.
The tectonic activity in the region is responsible for the formation of the Aleutian Islands over millions of years. As the Pacific Plate subducts beneath the North American Plate, magma is generated in the mantle and rises to the surface, resulting in the formation of new volcanic islands. This continuous process of volcanic activity has shaped the unique landscape of the Aleutian Islands.
Formation of the Aleutian Islands
The formation of the Aleutian Islands is a complex process that involves the interaction of various geological forces. It begins with the subduction of the Pacific Plate beneath the North American Plate along the Aleutian Trench.
As the Pacific Plate sinks into the mantle, it generates intense heat and pressure, causing the mantle to melt and form magma. This magma then rises to the surface through cracks and fissures in the Earth’s crust, leading to volcanic eruptions. Over time, these eruptions build up layers of lava and volcanic debris, gradually forming new islands.
The formation of the Aleutian Islands is also influenced by the movement of the tectonic plates. As the Pacific Plate continues to subduct beneath the North American Plate, it creates a zone of compression and uplift. This uplift, combined with the volcanic activity, contributes to the growth and expansion of the Aleutian Islands.
The formation of the Aleutian Islands is a fascinating geological process that spans millions of years. These islands, located in the northern Pacific Ocean, were formed as a result of intense tectonic activity in the region. The Aleutian Trench, a deep underwater trench, is a key feature in the formation of these islands. It is here that the Pacific Plate is subducted beneath the North American Plate, leading to the creation of volcanic arcs and the uplift of the islands.
Volcanic activity has played a crucial role in the formation of the Aleutian Islands. The islands are home to a chain of active volcanoes, which have erupted numerous times throughout history. These volcanic eruptions have contributed to the growth and expansion of the islands, as well as the creation of new landmasses.
Plate tectonics have had a significant impact on the Aleutian Islands. The ongoing subduction of the Pacific Plate beneath the North American Plate has resulted in the continued growth and evolution of the islands. This tectonic activity has also led to the formation of deep-sea trenches and the occurrence of earthquakes in the region.
In addition to tectonic activity, erosion and weathering processes have shaped the Aleutian Islands over time. The harsh climate and powerful ocean currents have eroded the coastlines and sculpted the landforms of the islands. These processes have created unique and diverse ecosystems, which support a wide range of plant and animal species.
The Aleutian Islands are not only geologically significant but also biologically diverse. The isolation of these islands has allowed for the development of unique ecosystems, with many endemic species found nowhere else in the world. The islands are home to a variety of marine mammals, birds, and fish, making them a hotspot for biodiversity.
Human presence on the Aleutian Islands dates back thousands of years, with indigenous peoples inhabiting the region for centuries. The islands have also been explored by European explorers and have played a role in various historical events, such as World War II.
In conclusion, the Aleutian Islands have a rich geological history, shaped by tectonic activity, volcanic eruptions, erosion, and weathering processes. These factors have contributed to the formation of the islands and the development of unique ecosystems. The islands continue to be a subject of scientific study and exploration, offering valuable insights into the Earth’s dynamic processes.Formation of the Aleutian Islands:
– The Aleutian Islands are a chain of volcanic islands located in the northern Pacific Ocean.
– These islands were formed as a result of intense tectonic activity in the region.
– The process of island formation began millions of years ago and is still ongoing today.
– The Aleutian Islands are situated along the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate.
– The collision and subduction of these two plates have led to the formation of the islands.
– Subduction occurs when one tectonic plate is forced beneath another, creating a deep trench and volcanic activity.
– The subduction of the Pacific Plate beneath the North American Plate has resulted in the formation of a volcanic arc, which includes the Aleutian Islands.
– The volcanic activity in the region has played a crucial role in the formation and growth of the islands.
– Over time, repeated volcanic eruptions have added layers of lava and ash, gradually building up the islands.
– The Aleutian Islands continue to experience volcanic activity, with several active volcanoes present in the chain.
Impact of Plate Tectonics on the Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands, located in the northern Pacific Ocean, have been greatly influenced by plate tectonics throughout their geological history. The movement of tectonic plates has played a significant role in the formation and shaping of these islands. Here are some key points to understand the impact of plate tectonics on the Aleutian Islands:
- Subduction Zone: The Aleutian Islands are situated along the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. This region is known as a subduction zone, where one tectonic plate is forced beneath another.
- Volcanic Arc: The subduction of the Pacific Plate beneath the North American Plate has resulted in the formation of a volcanic arc, known as the Aleutian Arc. This arc consists of a chain of volcanic islands, including the Aleutian Islands.
- Earthquakes: The collision and subduction of tectonic plates in the Aleutian region have led to frequent earthquakes. These earthquakes are often associated with the movement and interaction of the plates.
- Island Formation: The subduction of the Pacific Plate beneath the North American Plate has caused magma to rise to the surface, leading to the formation of new islands. Over time, volcanic activity has contributed to the growth and expansion of the Aleutian Islands.
- Island Migration: The movement of tectonic plates has also resulted in the migration of the Aleutian Islands. As the Pacific Plate continues to subduct beneath the North American Plate, the islands are gradually moving towards the mainland.
- Geological Hazards: The plate tectonic activity in the Aleutian region poses various geological hazards, including volcanic eruptions, tsunamis, and earthquakes. These hazards have significant implications for the local communities and infrastructure.
Overall, the impact of plate tectonics on the Aleutian Islands has been instrumental in their formation, growth, and ongoing geological processes. The dynamic nature of the region continues to shape these islands and influence their unique geological and ecological characteristics.
Erosion and Weathering Processes Shaping the Islands
The Aleutian Islands, located in the northern Pacific Ocean, have been shaped by various erosion and weathering processes over millions of years. These processes have played a significant role in sculpting the unique landscape of the islands.
One of the primary agents of erosion in the Aleutian Islands is water. The constant action of waves crashing against the rocky shores has gradually worn away the coastline, creating cliffs and sea caves. Additionally, rivers and streams have carved deep valleys and canyons as they flow through the islands, further shaping the land.
Weathering, on the other hand, refers to the breakdown of rocks and minerals on the surface. The Aleutian Islands experience a harsh climate, with strong winds, freezing temperatures, and frequent storms. These weather conditions contribute to the physical and chemical weathering of rocks, causing them to break apart and form sediment.
Glaciers have also played a significant role in shaping the Aleutian Islands. During the last ice age, massive glaciers covered the region, scouring the land and leaving behind deep U-shaped valleys and fjords. As the glaciers retreated, they deposited large amounts of sediment, creating moraines and shaping the landscape further.
Overall, the erosion and weathering processes in the Aleutian Islands have resulted in a diverse and rugged terrain, characterized by steep cliffs, deep valleys, and unique geological formations. These processes continue to shape the islands today, contributing to their ever-changing and dynamic nature.
Biodiversity and unique ecosystems of the Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands, located in the northern Pacific Ocean, are not only geologically fascinating but also home to a diverse range of ecosystems and unique biodiversity. These islands, formed through a combination of tectonic activity and volcanic eruptions, have created a variety of habitats that support a wide array of plant and animal species.
One of the most notable features of the Aleutian Islands is their rich marine life. The surrounding waters are teeming with fish, including salmon, halibut, and cod, which attract larger predators such as sea lions and orcas. The islands also serve as important breeding grounds for seabirds, including puffins, auklets, and cormorants.
On land, the Aleutian Islands are characterized by rugged terrain and harsh weather conditions. Despite these challenges, a number of plant species have adapted to thrive in this environment. Mosses, lichens, and grasses can be found clinging to rocky cliffs, while hardy shrubs and wildflowers dot the landscape.
The unique ecosystems of the Aleutian Islands are not only important for their biodiversity but also for their ecological role. These islands provide nesting sites for migratory birds, act as nurseries for marine species, and contribute to the overall health of the surrounding marine ecosystem.
In conclusion, the Aleutian Islands are not only geologically significant but also host a remarkable array of biodiversity and unique ecosystems. The delicate balance of these ecosystems must be protected to ensure the continued survival of the diverse plant and animal species that call these islands home.
Human presence and exploration of the islands
The Aleutian Islands have a long history of human presence and exploration. The islands have been inhabited by indigenous peoples for thousands of years, with evidence of human settlement dating back at least 9,000 years. The Aleut people, who gave the islands their name, have a rich cultural heritage and have relied on the islands’ resources for their survival.
In more recent history, the islands have been explored and settled by Europeans. Russian fur traders arrived in the 18th century, establishing trading posts and exploiting the islands’ fur-bearing animals. The islands were later sold to the United States as part of the Alaska Purchase in 1867.
Today, the Aleutian Islands are home to several communities, with the largest being Unalaska. These communities rely on fishing, tourism, and other industries for their livelihoods. The islands also have strategic military importance, with several military bases located there.
The exploration and settlement of the Aleutian Islands have had a significant impact on the islands’ ecosystems and biodiversity. Introduced species, such as rats and foxes, have had devastating effects on native wildlife. Efforts are now being made to protect and restore the islands’ unique ecosystems.
Conclusion: The Aleutian Islands, with their rich geological history and unique ecosystems, have been shaped by a combination of tectonic activity, volcanic eruptions, erosion, and weathering processes. These islands, located in the northern Pacific Ocean, have been formed over millions of years through the collision of tectonic plates and the subsequent volcanic activity. The ongoing subduction of the Pacific Plate beneath the North American Plate has resulted in the formation of a chain of volcanic islands, stretching over 1,200 miles.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the Aleutian Islands are a testament to the dynamic nature of our planet. The geological processes that have shaped these islands over millions of years continue to shape them today. The volcanic activity, tectonic movements, erosion, and weathering processes have all played a role in creating the unique landscapes and ecosystems found in the Aleutian Islands. These islands are not only a geological wonder but also a haven for biodiversity, with numerous unique species calling them home. As human presence and exploration of the islands continue, it is important to recognize and appreciate the delicate balance between human activities and the preservation of these fragile ecosystems.
Discover the fascinating geological history and formation of the Aleutian Islands, shaped by tectonic activity and volcanic eruptions.
About The Author

Alison Sowle is the typical tv guru. With a social media evangelist background, she knows how to get her message out there. However, she's also an introvert at heart and loves nothing more than writing for hours on end. She's a passionate creator who takes great joy in learning about new cultures - especially when it comes to beer!